Introduction to Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining is a cornerstone of employer-employee relations, involving negotiations between employers (or their associations) and employee representatives, typically trade unions, to determine terms of employment such as wages, working hours, conditions, and benefits. It results in a collective agreement that is legally binding for a specified period, promoting industrial harmony and worker empowerment. In India, collective bargaining has evolved from colonial-era labor struggles to a structured process under modern labor laws, notably the Industrial Relations Code, 2020, which consolidates the Trade Unions Act, 1926, and the Industrial Disputes Act, 1947. The process reflects the constitutional ethos of social justice, enshrined in Articles 19(1)(c) (right to form associations) and 43A (worker participation in management). For UPSC EPFO (Enforcement Officer/Accounts Officer, Assistant Provident Fund Commissioner) and UPSC ALC (Assistant Labour Commissioner) exams, collective bargaining is a critical topic under “Industrial Relations & Labour Laws,” with high weightage due to its role in dispute prevention and labor welfare. This study material provides a detailed exploration of its concepts, legal framework, processes, challenges, and exam-relevant aspects, including case laws and recent reforms.
Key Concepts of Collective Bargaining
Definition and Objectives
Collective bargaining is a bipartite or tripartite negotiation process where employers and employee representatives agree on employment terms, aiming to balance organizational goals with worker welfare. Its objectives include:
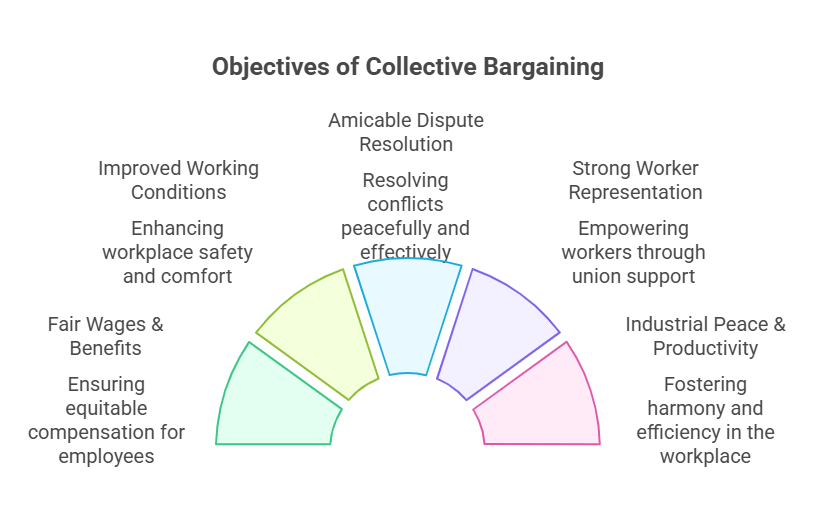
The process is rooted in mutual consent and good-faith negotiations, distinguishing it from individual bargaining, which lacks collective strength.
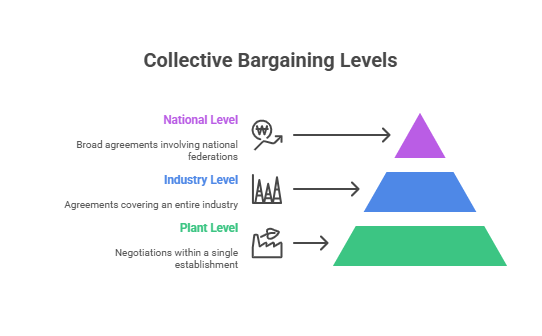
Levels of Collective Bargaining
Collective bargaining occurs at multiple levels, each with distinct scopes and implications:
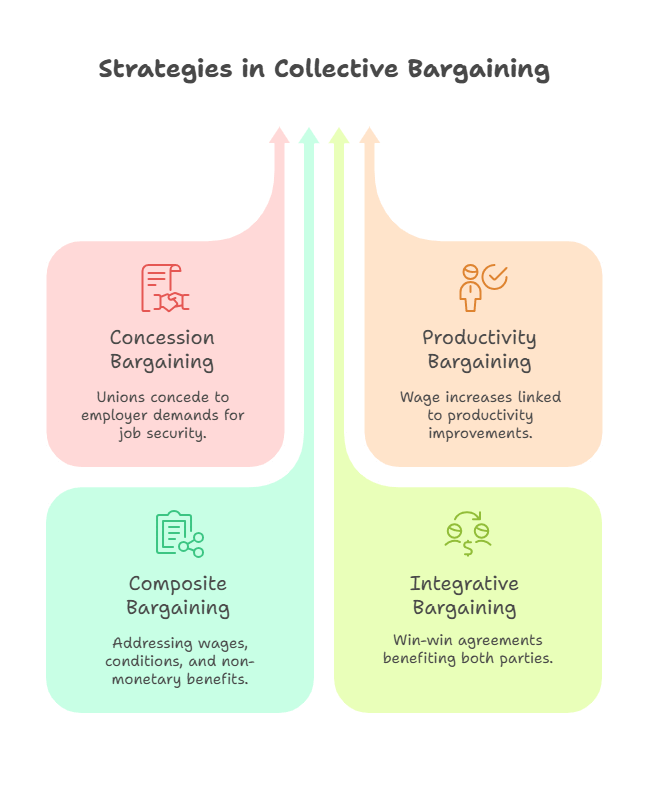
Types of Collective Bargaining
Legal Framework
The Industrial Relations Code, 2020, governs collective bargaining in India, replacing older laws. Key provisions include:
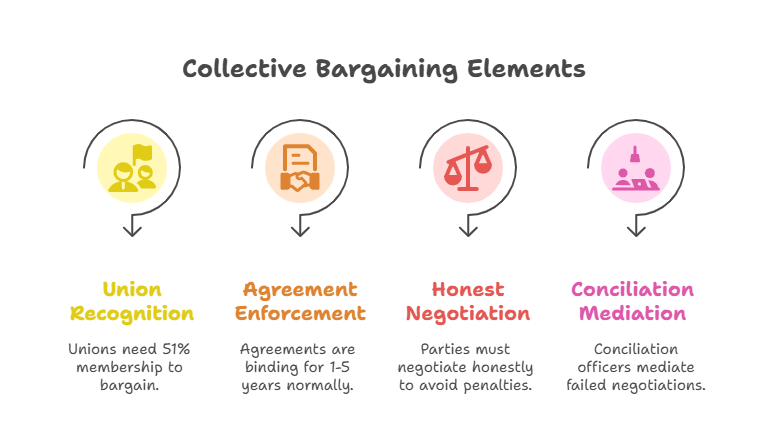
The Code aligns with ILO Convention 98 (Right to Organise and Collective Bargaining), though India has not ratified it, a point often tested in ALC exams.
| Aspect | Details | Exam Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Negotiation between employer and union for terms | EPFO: Dispute prevention; ALC: Union role |
| Levels | Plant, industry, national | Questions on scope and examples |
| Types | Concession, productivity, composite, integrative | Link to case studies, sectors |
| Legal Framework | IR Code 2020; recognition, binding agreements | Focus on provisions, ILO links |
Process of Collective Bargaining
The collective bargaining process in India follows a structured approach:
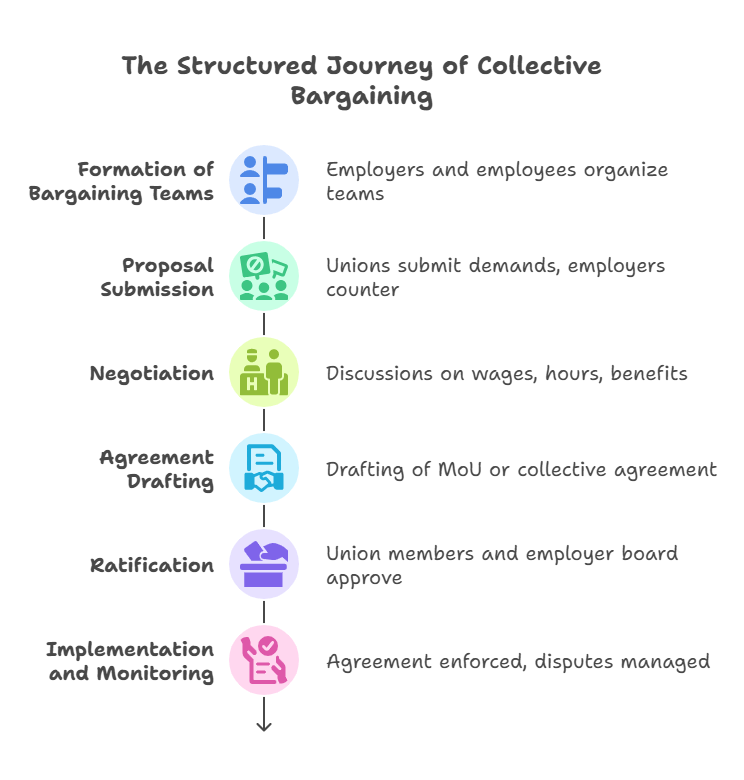
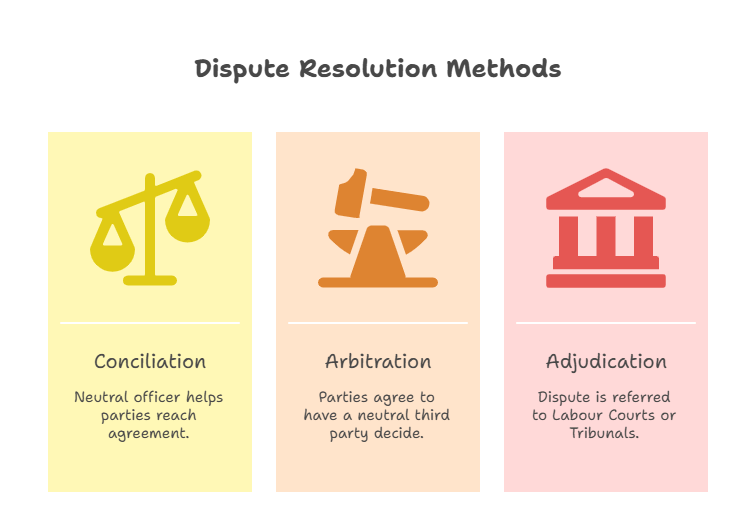
If negotiations fail, the IR Code provides for:
Case Law: Ram Prasad Vishwakarma v. Chairman, Industrial Tribunal (1961) – Supreme Court held that collective agreements are binding if fair and voluntary, emphasizing good-faith negotiation.
Historical Evolution in India
Collective bargaining in India evolved through distinct phases:
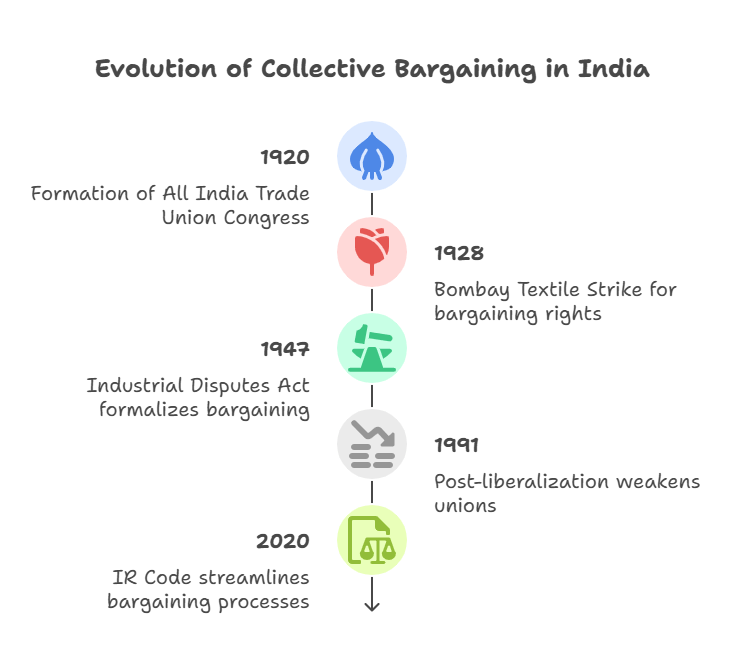
Key Milestone: The Trade Unions Act, 1926, granted legal recognition, enabling bargaining. Case: B.R. Singh v. Union of India (1989) – Right to unionize as fundamental under Article 19(1)(c).
Key Features of Collective Bargaining under IR Code, 2020
| Feature | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Negotiating Union | 51% membership for recognition | Reduces multiple unions; strengthens representation |
| Agreement Duration | 1-5 years, extendable | Ensures stability; prevents frequent disputes |
| Good-Faith Clause | Mandatory honest negotiations | Penalties for refusal; promotes trust |
| Dispute Resolution | Conciliation, arbitration, tribunals | Prevents strikes; quick resolution |
| Strike/Lockout Rules | 60-day notice, no work stoppage during conciliation | Balances rights; minimizes disruptions |
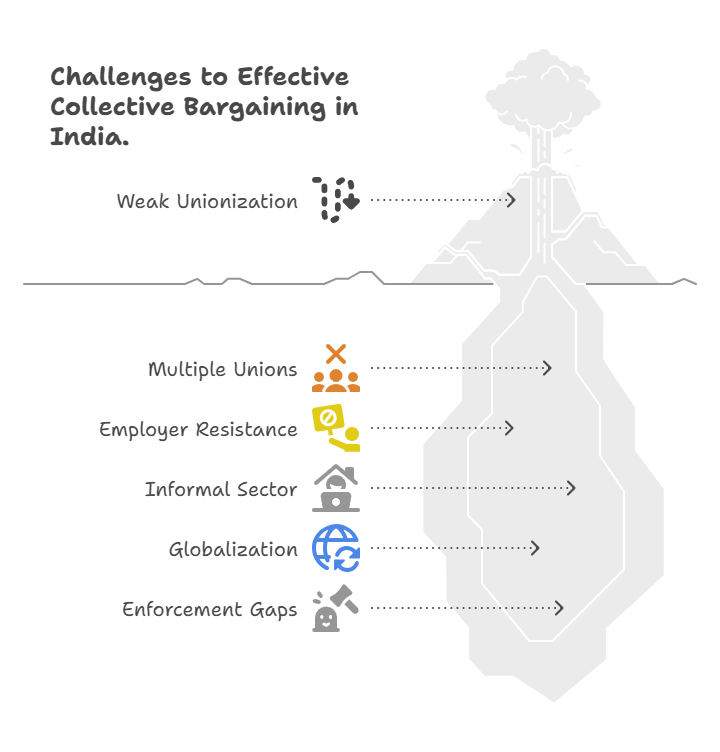
Challenges in Collective Bargaining
Major Case Laws on Collective Bargaining
Relevance to UPSC EPFO and ALC Exams
UPSC EPFO (EO/AO/APFC)
- Syllabus Link: Industrial Relations (IR Code, bargaining processes), Labour Laws (dispute prevention, social security impact).
- Weightage: 15-20% of paper; 10-15 MCQs on concepts, laws, cases.
- Focus Areas:
- Role of bargaining in reducing disputes affecting PF compliance.
- Link to social security (e.g., wage definitions for EPF contributions).
- Case laws on agreements, strikes.
- Question Types: MCQs on provisions, case-based scenarios, short notes on bargaining levels.
UPSC ALC
- Syllabus Link: Industrial Relations (IR Code, union recognition), Labour Welfare (worker empowerment), Trade Union Movement.
- Weightage: 40-50%; 20-25 MCQs, 4-6 descriptive questions.
- Focus Areas:
- Union role in bargaining, negotiation councils.
- Legal framework (IR Code vs. old acts).
- Challenges in unorganized sectors, gig economy.
- Case laws on union rights, agreement enforcement.
- Question Types: Descriptive on bargaining process, challenges; MCQs on legal provisions, cases.
| Exam | Syllabus Focus | Weightage | Key Topics | Preparation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPFO | Industrial Relations, Labour Laws | 15-20% | Bargaining, disputes, social security | Study IR Code, case laws; practice MCQs |
| ALC | Industrial Relations, Labour Welfare, Trade Unions | 40-50% | Union recognition, bargaining challenges | Focus on legal provisions, descriptive answers, current reforms |


Leave a comment