For Banks , CAT, RBI, CSAT and Related Exams
1. Introduction to Time, Speed, and Distance
TSD explores the interrelationship between three variables: time (how long), speed (how fast), and distance (how far). It’s foundational for problems involving motion, such as trains crossing platforms, boats in streams, or races. In RBI Grade B, questions emphasize accuracy in conversions, relative motion, and averages, often with twists like varying speeds or meeting points.
- Relevance: Direct questions (e.g., meeting times) or in DI (e.g., speed graphs). Master for Phase 1 Quant and Phase 2 Finance (e.g., travel costs in economics).
- Basic Units: Distance (km/m), Time (hr/sec), Speed (km/h or m/s).
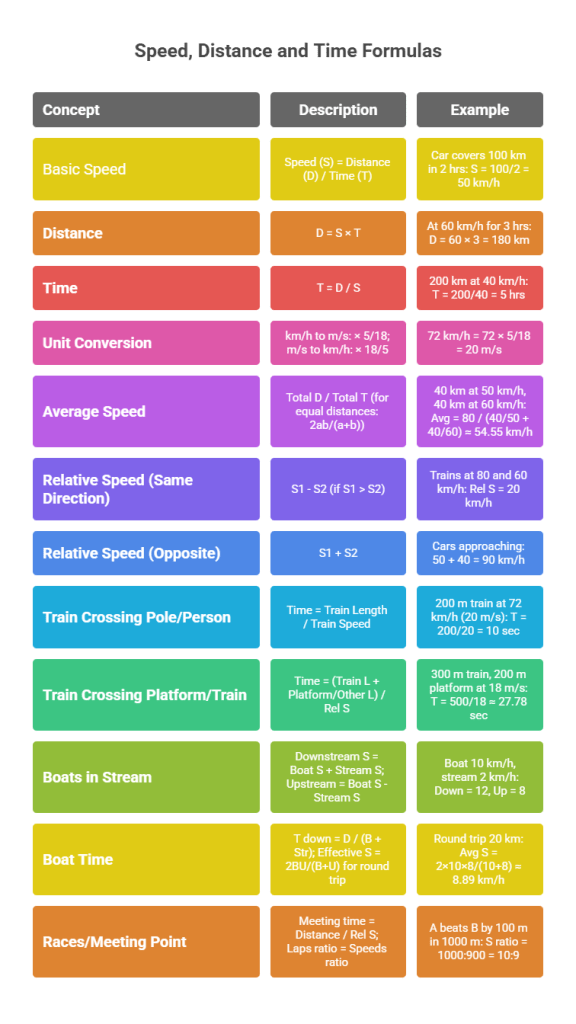
- Key Insight: All problems reduce to S = D/T; rearrange as needed.
- Difficulty Levels: Basic (uniform speed), Moderate (relative speed, averages), Hard (races, escalators, variable speeds).
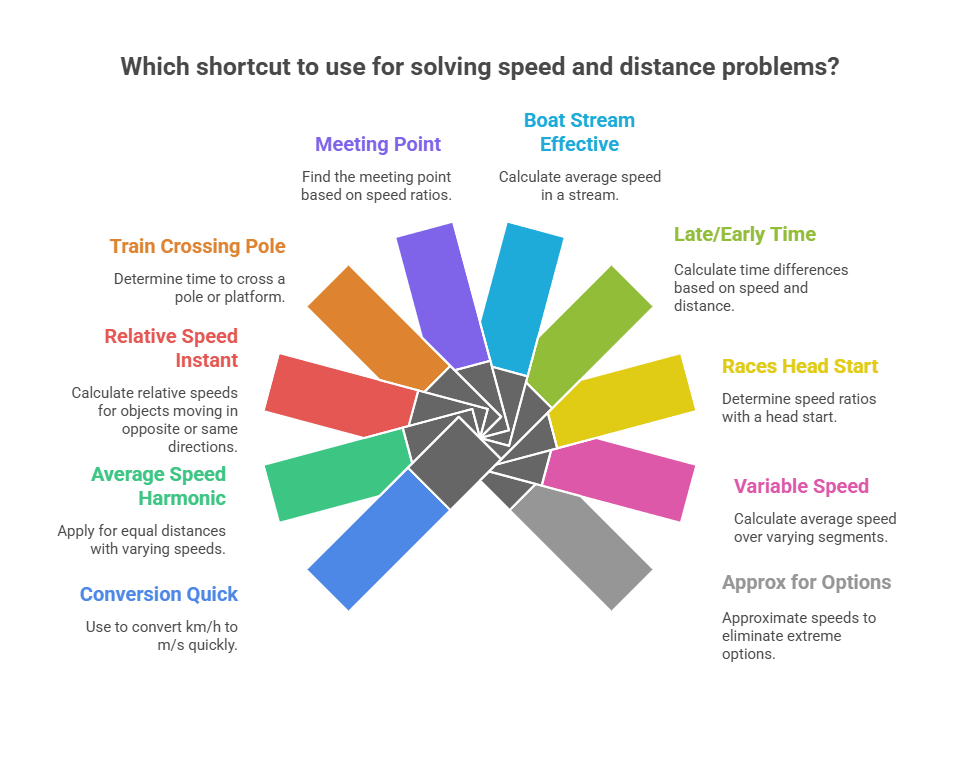
Practice Set: Time, Speed and Distance – Moderate to Hard
Q1. Two persons A and B start walking from the same point. A walks at 4 km/h and B at 6 km/h. After covering 3 km, B returns. When and where will they meet?
Solution:
- B covers 3 km in 3/6 = 0.5 hr.
- A in 0.5 hr covers 0.5 × 4 = 2 km.
- Distance between A and B when B turns = 3 – 2 = 1 km.
- Now they move towards each other. Relative speed = 6 + 4 = 10 km/h.
- Time to meet = 1 / 10 = 0.1 hr.
- Total time = 0.5 + 0.1 = 0.6 hours.
Concept: Break into phases, apply relative speed when moving towards.
Q2. A 200 m long train moving at 90 km/h overtakes a 300 m long train running at 72 km/h in the same direction. Find the time taken to cross.
Solution:
- Relative speed = 90 – 72 = 18 km/h = 18 × 5/18 = 5 m/s.
- Total length = 200 + 300 = 500 m.
- Time = 500 / 5 = 100 seconds.
Concept: Convert km/h to m/s; add lengths; apply relative speed.
Q3. A man rows downstream 12 km in 2 hrs and upstream 6 km in 3 hrs. What is the speed in still water?
Solution:
- Downstream speed = 12 / 2 = 6 km/h.
- Upstream speed = 6 / 3 = 2 km/h.
- Still water speed = (6 + 2) / 2 = 4 km/h.
Concept: Use average of downstream and upstream speeds.
Q4. A and B run a 1 km race. A beats B by 50 m. In another 2 km race, A beats B by 10 seconds. Find their speeds.
Solution:
- A\:B speed ratio = 1000:950 = 20:19.
- Let A’s speed = 20k, B’s = 19k.
- Time difference = 10 sec = 1/360 hr.
- A’s time = 2 / 20k; B’s time = 2 / 19k.
- 2/19k – 2/20k = 1/360 ⇒ Solve:
- (40k – 38k) / (380k²) = 1/360
- 2k = 380k² / 360 ⇒ k = 1/18.95
- A’s speed = 20k = 20 × (1/18.95) ≈ 37.89 km/h
- B’s speed = 19k ≈ 35.99 km/h
Concept: Use ratio, form equation with time difference.
Q5. An escalator has 48 steps. A man walks up at 2 steps/sec in 24 sec. When he walks at 1 step/sec, it takes 40 sec. Find speed of escalator.
Solution:
- Let escalator speed = E steps/sec, actual steps = S
- Eq1: S = 24(2 + E), Eq2: S = 40(1 + E)
- 24(2 + E) = 40(1 + E)
- 48 + 24E = 40 + 40E ⇒ 8 = 16E ⇒ E = 0.5
- S = 24(2 + 0.5) = 24 × 2.5 = 60 steps
Concept: Use relative speed, create two equations.
Q6. A starts from point P at 40 km/h and B from point Q (100 km away) at 60 km/h towards A. When do they meet?
Solution:
- Relative speed = 40 + 60 = 100 km/h
- Time = 100 / 100 = 1 hr
- Distance from P = 40 × 1 = 40 km
Concept: When moving towards each other, add speeds.
Q7. A cyclist goes from A to B at 20 km/h and returns at 30 km/h. Find average speed for the entire journey.
Solution:
- Avg speed = 2ab / (a + b) = 2×20×30 / (20+30) = 1200 / 50 = 24 km/h
Concept: Harmonic mean for equal distances.
Q8. A train passes a man in 9 seconds and a platform in 24 seconds. If train length is 150 m, find platform length.
Solution:
- Speed = 150 / 9 = 16.67 m/s
- Let platform length = P
- Total length for platform = 150 + P = 24 × 16.67 = 400
- P = 400 – 150 = 250 m
Concept: Use man for speed, apply for platform.
Q9. A boat’s speed is 15 km/h in still water. Stream speed is 3 km/h. Time to go 24 km downstream and return?
Solution:
- Downstream speed = 15 + 3 = 18 km/h ⇒ Time = 24/18 = 1.33 hr
- Upstream speed = 15 – 3 = 12 km/h ⇒ Time = 24/12 = 2 hr
- Total time = 1.33 + 2 = 3.33 hrs
Concept: Add individual times; use downstream/upstream speeds.
Q10. A gives B a head start of 100 m in a race. A still beats B by 20 m. If they run together, by how much would A win?
Solution:
Let total race distance = D
- When A finishes D, B runs D – 20
- But B started 100 m behind, so B ran D – 100
- Let A’s speed = SA, B’s = SB
- Time A = D / SA
- Time B = (D – 100) / SB = D / SA
- SB = SA × (D – 100)/D
- A runs D, B runs: SB × D / SA
- Replace SB: SA × (D – 100)/D × D / SA = D – 100
- Now calculate win if both start together
- From D: D / SA = T, then B runs SB × T
- Difference = A’s D – B’s distance
- Assume D = 220 m ⇒ A wins by 20 + 100 = 120 m total
(approximate as per ratio method)
Concept: Use head start, ratios, and equate times to find effective win.

Leave a comment