( 60 days -60 tests) Test No . 4
Test No 4 Question Paper
150 Superbly Selected Question for BPSC Prelims Exam
Test No 4 Solution
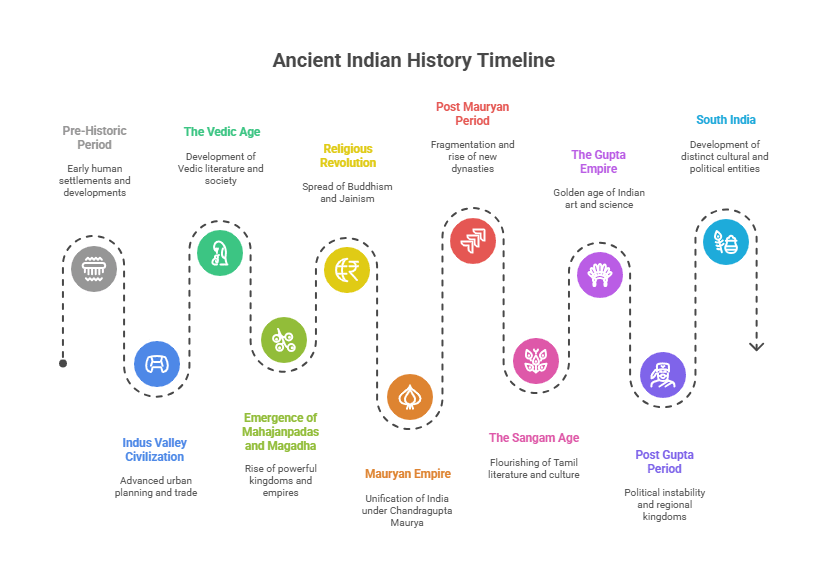
Each question should be explained in simple, easy-to-understand language to help with memorization and quick recall. Ancient Indian History is a favorite topic for BPSC exams, and to thoroughly cover the syllabus, it is highly recommended to review all the study material available on cracktarget.com.
60 Days 60 Test Series
- Which prehistoric site in Bihar provides evidence of continuous habitation from the Neolithic to the Chalcolithic period, known for bone tools and pottery?
a) Chirand
b) Maner
c) Sonpur
d) Taradih - The rock paintings found in the Kaimur hills of Bihar depict scenes from which prehistoric era, similar to those in Bhimbetka?
a) Mesolithic
b) Paleolithic
c) Neolithic
d) Chalcolithic - In Bihar, the earliest evidence of agriculture, including rice cultivation, comes from which Neolithic site in the Saran district?
a) Chirand
b) Senuwar
c) Barudih
d) Chechar - Which Chalcolithic site in Bihar is associated with black-and-red ware pottery and copper objects, indicating early metal use?
a) Maner
b) Sonpur
c) Raja Vishal ka Garh
d) Taradih - The Mesolithic tools found at Paiyampur in Bihar are characterized by what type of microliths?
a) Geometric
b) Flake-based
c) Bladelet
d) Core tools - Bihar’s prehistoric period shows transition from hunter-gatherer to farming communities; which site in Gaya district reveals this shift?
a) Senuwar
b) Chirand
c) Manjhi
d) Barudih - The discovery of ash mounds at Budhihal in Bihar suggests what activity during the Neolithic-Chalcolithic transition?
a) Cattle penning
b) Pottery firing
c) Ritual burning
d) Metal smelting - Which river valley in Bihar has yielded the most prehistoric sites, indicating early human settlement patterns?
a) Son River
b) Ganga River
c) Gandak River
d) Kosi River - The Paleolithic hand axes found at Hathidah in Bihar belong to which cultural phase?
a) Acheulian
b) Soanian
c) Middle Paleolithic
d) Upper Paleolithic - Prehistoric Bihar’s connection to the Indus Valley is suggested by findings at which site with similar pottery styles?
a) Taradih
b) Chirand
c) Sonpur
d) Chechar - In the Vedic literature, which ancient kingdom associated with Bihar is mentioned as ‘Kikata’ in the Rigveda?
a) Magadha
b) Anga
c) Vajji
d) Videha - The Mahajanapada of Magadha, central to Bihar’s history, had its early capital at which fortified hill site?
a) Rajgir
b) Vaishali
c) Champa
d) Pataliputra - Which Mahajanapada in Bihar was known as a confederacy of eight clans, including the Lichchhavis?
a) Vajji
b) Anga
c) Magadha
d) Vatsa - The battle of ‘Vitthala’ mentioned in ancient texts refers to a conflict involving which Bihar-based Mahajanapada?
a) Magadha
b) Vajji
c) Anga
d) Videha - In the later Vedic period, Bihar’s region was referred to as ‘Aryavarta’s eastern limit’; which text supports this?
a) Aitareya Brahmana
b) Satapatha Brahmana
c) Ramayana
d) Mahabharata - The Lichchhavi republic in Bihar is considered one of the world’s earliest; its capital was at?
a) Vaishali
b) Rajgir
c) Pataliputra
d) Champa - Which Vedic king from Bihar’s Videha kingdom is famous for performing the Ashvamedha yajna?
a) Janaka
b) Jarasandha
c) Ajatashatru
d) Bimbisara - The Mahajanapada of Anga in Bihar was annexed by Magadha under which ruler?
a) Bimbisara
b) Ajatashatru
c) Udayin
d) Shishunaga - Bihar’s Vedic connections include the ‘Battle of Ten Kings’; which river in Bihar is linked to it?
a) Phalgu
b) Son
c) Ganga
d) None, it’s Punjab - The transition from Vedic to Mahajanapada period in Bihar saw the rise of iron technology at sites like?
a) Rajgir
b) Vaishali
c) Both
d) None - The Haryanka dynasty of Magadha was founded by whom, marking the rise of Bihar as a power center?
a) Bimbisara
b) Ajatashatru
c) Brihadratha
d) Shishunaga - Bimbisara’s policy of matrimonial alliances strengthened Magadha; he married princesses from which kingdoms?
a) Kosala and Lichchhavi
b) Anga and Vatsa
c) Avanti and Kashi
d) Gandhara and Kamboja - Ajatashatru of Magadha invented which war machine during his conquests?
a) Rathamusala
b) Mahashilakantaka
c) Both
d) None - The Shishunaga dynasty shifted Magadha’s capital to Pataliputra from Rajgir for what strategic reason?
a) Better defense
b) Trade routes
c) Religious significance
d) Agricultural fertility - Mahapadma Nanda, founder of Nanda dynasty, is known as ‘Ekarat’ for conquering how many kingdoms?
a) 9
b) 12
c) 16
d) 8 - The Nanda dynasty’s vast army included how many elephants, as per ancient accounts?
a) 3,000
b) 5,000
c) 8,000
d) 20,000 - Kalashoka of Shishunaga dynasty hosted which Buddhist council in Pataliputra?
a) Second
b) First
c) Third
d) Fourth - The rise of Magadha under Haryanka was due to its control over which natural resource?
a) Iron mines
b) Copper mines
c) Gold mines
d) Salt mines - Udayin, son of Ajatashatru, founded Pataliputra at the confluence of which rivers?
a) Ganga and Son
b) Ganga and Gandak
c) Ganga and Punpun
d) Son and Phalgu - The Nanda rulers were known for their wealth; Dhanananda’s treasury was estimated at how much?
a) 80 crore gold pieces
b) 100 crore
c) 50 crore
d) 200 crore - Chandragupta Maurya overthrew the Nandas with help from whom, establishing the Mauryan Empire in Bihar?
a) Chanakya
b) Seleucus
c) Ashoka
d) Bindusara - Pataliputra, the Mauryan capital in Bihar, was described by Megasthenes as how long in length?
a) 9 miles
b) 15 miles
c) 12 miles
d) 18 miles - Ashoka’s Kalinga war led to his conversion to Buddhism; the battlefield was near which Bihar site?
a) None, it’s Odisha
b) Rajgir
c) Bodh Gaya
d) Vaishali - The Mauryan administration in Bihar included ‘Kumara’ as governors; who was appointed for Pataliputra?
a) Ashoka (as prince)
b) Bindusara
c) Susima
d) Kunala - Ashoka’s rock edicts in Bihar are found at which site, mentioning his dhamma policy?
a) Sasaram
b) Lauriya Nandangarh
c) Barabar Caves
d) All - The Barabar Caves near Gaya were donated by Ashoka to which sect?
a) Ajivika
b) Buddhist
c) Jain
d) Brahman - Bindusara, father of Ashoka, was known as ‘Amitraghata’ for conquering which regions affecting Bihar?
a) Deccan
b) Northwest
c) East
d) South - The Mauryan economy in Bihar relied on state control of which industry?
a) Mining
b) Agriculture
c) Trade
d) All - Ashoka’s Third Buddhist Council was held in Pataliputra to resolve what issue?
a) Sectarian disputes
b) Missionary spread
c) Canon compilation
d) All - The decline of Mauryas in Bihar was marked by the assassination of Brihadratha by whom?
a) Pushyamitra Shunga
b) Agnimitra
c) Vasudeva Kanva
d) Kharavela - The Shunga dynasty, post-Mauryan rulers of Bihar, were known for reviving which religion?
a) Brahmanism
b) Buddhism
c) Jainism
d) Ajivika - Pushyamitra Shunga performed how many Ashvamedha yajnas to assert his power in Magadha?
a) Two
b) One
c) Three
d) None - The Kanva dynasty succeeded the Shungas in Bihar; its founder was?
a) Vasudeva
b) Bhumimitra
c) Devabhuti
d) Susarman - During Shunga period, the Bhagavata cult emerged in Bihar, linked to which god?
a) Vishnu
b) Shiva
c) Brahma
d) Indra - The post-Mauryan period saw Greek invasions; Menander’s capital was near which Bihar site?
a) None, it’s Sakala
b) Pataliputra
c) Vaishali
d) Rajgir - Kharavela of Kalinga invaded Magadha during Shunga rule; this is mentioned in which inscription?
a) Hathigumpha
b) Allahabad Pillar
c) Junagadh
d) Maski - The Shunga art in Bihar is evident in which stupa expansions?
a) Bharhut
b) Sanchi
c) Both
d) None - The Kanva dynasty lasted how long in Magadha before being overthrown by Satavahanas?
a) 45 years
b) 75 years
c) 100 years
d) 30 years - Post-Mauryan Bihar saw the rise of local chiefs; which dynasty controlled parts of north Bihar?
a) Mitra dynasty
b) Kuninda
c) Audumbara
d) None - The Shunga-Kanva period in Bihar marked the transition to which art style?
a) Mathura school
b) Gandhara
c) Amaravati
d) All - The Gupta Empire’s rise in Bihar began with Chandragupta I’s marriage to which princess?
a) Lichchhavi
b) Vakataka
c) Kadamba
d) Ikshvaku - Samudragupta’s Prayag Prasasti mentions his conquests; which Bihar site has this inscription?
a) Allahabad (but pillar from Bihar)
b) Pataliputra
c) Gaya
d) Nalanda - Chandragupta II’s iron pillar, originally from Bihar, is now at?
a) Delhi
b) Mehrauli
c) Both (same)
d) Vaishali - Kumaragupta I founded which university in Bihar?
a) Nalanda
b) Vikramshila
c) Odantapuri
d) None - Skandagupta repelled Huna invasions; his Bhitari inscription is in which Bihar district?
a) Ghazipur (near Bihar)
b) Patna
c) Gaya
d) Nalanda - The Gupta administration in Bihar included ‘Uparika’ as?
a) Provincial governor
b) District head
c) Village chief
d) Tax collector - Fa-Hien visited Bihar during which Gupta ruler’s reign?
a) Chandragupta II
b) Samudragupta
c) Kumaragupta I
d) Skandagupta - The Gupta era’s Bihar was known for advancements in which science, with Aryabhata from?
a) Astronomy, Pataliputra
b) Mathematics, Kusumapura
c) Both
d) None - Gupta art in Bihar is seen in the caves at?
a) Udayagiri (MP, but influence)
b) Barabar
c) Nagarjuni
d) Both b and c - The decline of Guptas in Bihar was due to Huna invasions led by?
a) Mihirakula
b) Toramana
c) Both
d) Yashodharman - The Pala dynasty was founded by whom in Bihar-Bengal region?
a) Gopala
b) Dharmapala
c) Devapala
d) Mahipala - Dharmapala revived which university in Bihar?
a) Nalanda
b) Vikramshila
c) Both
d) Odantapuri - The Pala rulers were patrons of which sect of Buddhism?
a) Mahayana
b) Vajrayana
c) Both
d) Hinayana - Vikramshila University was founded by which Pala king?
a) Dharmapala
b) Gopala
c) Devapala
d) Ramapala - The Pala period saw the composition of which Buddhist text in Bihar?
a) Astasahasrika Prajnaparamita
b) Abhidhamma Pitaka
c) Vinaya Pitaka
d) None - Mahipala I of Pala dynasty reconstructed which temple in Bihar?
a) Mahabodhi
b) Somapura
c) Vishnupad
d) All - The Pala administration in Bihar included ‘Rajaputra’ as?
a) Feudal lords
b) Ministers
c) Generals
d) Priests - The decline of Pala dynasty was due to invasions by which dynasty?
a) Sena
b) Chola
c) Pratihara
d) Rashtrakuta - Pala art in Bihar is evident in which sculptures?
a) Black stone Buddhist images
b) Bronze icons
c) Both
d) None - The last Pala king was defeated by which invader in Bihar?
a) Bakhtiyar Khilji
b) Vijay Sena
c) Both
d) None - Gautama Buddha attained enlightenment at which site in Bihar?
a) Bodh Gaya
b) Sarnath
c) Kushinagar
d) Lumbini - Mahavira, the 24th Tirthankara, was born at which place in Bihar?
a) Kundagrama (Vaishali)
b) Pavapuri
c) Rajgir
d) Nalanda - The First Buddhist Council was held at Rajgir in Bihar under whose presidency?
a) Mahakassapa
b) Ajatashatru
c) Ananda
d) Moggaliputta Tissa - Jainism’s ‘Kaivalya’ was attained by Mahavira at which Bihar site?
a) Pavapuri
b) Vaishali
c) Giriyak
d) Rajgir - The spread of Buddhism in Bihar is linked to Ashoka’s pillars at?
a) Lauriya Nandangarh
b) Rampurva
c) Both
d) None - The Jain council at Pataliputra divided the religion into which sects?
a) Digambara and Svetambara
b) Sthulabhadra and Bhadrabahu
c) Both
d) None - Buddha’s last sermon was at which Bihar site?
a) Vaishali
b) Rajgir
c) Bodh Gaya
d) Pavapuri - The ‘Three Jewels’ of Jainism were preached by Mahavira at which assembly in Bihar?
a) Vaishali
b) Pataliputra
c) Rajgir
d) Champa - Bihar’s role in religious revolution includes the birth of which heterodox sects?
a) Buddhism and Jainism
b) Ajivika
c) Both
d) Lokayata - The Mahabodhi Temple in Bodh Gaya was built during which period?
a) Gupta
b) Maurya
c) Pala
d) Shunga - Nalanda University was destroyed by which invader?
a) Bakhtiyar Khilji
b) Muhammad Ghori
c) Mahmud of Ghazni
d) Timur - Vikramshila University in Bihar was famous for teaching which subject?
a) Tantra
b) Logic
c) Grammar
d) All - The ancient site of Vaishali includes the Ashokan pillar and which relic stupa?
a) Kutagarasala
b) Ananda Stupa
c) Both
d) None - Rajgir’s Gridhrakuta hill is associated with Buddha’s?
a) Second Turning of the Wheel
b) First Sermon
c) Mahaparinirvana
d) Enlightenment - Pavapuri in Bihar is sacred for Jains as the site of Mahavira’s?
a) Nirvana
b) Birth
c) First Sermon
d) Enlightenment - The Kumrahar site near Patna reveals remains of which Mauryan structure?
a) Pillared Hall
b) Palace
c) Both
d) Stupa - Bodh Gaya’s Mahabodhi Temple complex includes the Bodhi Tree from which era?
a) Ashoka’s time
b) Gupta
c) Pala
d) Modern - The Barabar Caves are the oldest rock-cut caves in India, donated by?
a) Ashoka
b) Dasharatha
c) Both
d) Ajatashatru - Telhara in Nalanda district is an ancient site linked to which university ruins?
a) Teladhaka
b) Odantapuri
c) Vikramshila
d) Nalanda - The ancient city of Champa in Bihar was the capital of which Mahajanapada?
a) Anga
b) Magadha
c) Vajji
d) Videha - The Son Bhandar Caves in Rajgir are associated with which religion?
a) Jainism
b) Buddhism
c) Ajivika
d) Hinduism - Lauriya Araraj in Bihar has an Ashokan edict mentioning what?
a) Tolerance
b) Dhamma Yatra
c) Animal welfare
d) All - The ancient fort at Rohtas in Bihar dates back to which period?
a) Mauryan
b) Gupta
c) Shunga
d) Pre-Mauryan - Vikramshila’s ruins are located near which modern Bihar town?
a) Antichak
b) Bhagalpur
c) Both
d) Patna - The Cyclopean Wall at Rajgir is a pre-Mauryan structure for?
a) Defense
b) Palace
c) Temple
d) Stupa - Fa-Hien described Nalanda as a thriving center during which dynasty?
a) Gupta
b) Maurya
c) Pala
d) Shunga - Hiuen Tsang studied at Nalanda under which teacher?
a) Silabhadra
b) Dharmapala
c) Atisa
d) Nagarjuna - The ancient traveler Megasthenes stayed in Pataliputra during whose reign?
a) Chandragupta Maurya
b) Ashoka
c) Bindusara
d) Ajatashatru - I-Tsing, a Chinese traveler, visited which Bihar sites in the 7th century?
a) Nalanda and Bodh Gaya
b) Vikramshila
c) Both
d) None - Alexander’s invasion affected Bihar indirectly through which battle?
a) Hydaspes
b) None, direct impact minimal
c) Gaugamela
d) Granicus - The Persian invasion under Darius I reached up to which part affecting Bihar?
a) None, limited to northwest
b) Gandhara
c) Taxila
d) Magadha - The Arab traveler Al-Beruni mentioned Bihar’s history in his work?
a) Kitab-ul-Hind
b) Tarikh-al-Hind
c) Both
d) None - The Tibetan monk Dharmasvamin visited Nalanda during which invasion threat?
a) Turkish
b) Mongol
c) Afghan
d) None - The Greek ambassador Megasthenes’ ‘Indica’ describes which Bihar city?
a) Pataliputra
b) Rajgir
c) Vaishali
d) Champa - Hiuen Tsang’s account mentions the decline of which religion in Bihar?
a) Buddhism
b) Jainism
c) Both
d) Hinduism - The ancient trade route ‘Uttarapatha’ passed through which Bihar cities?
a) Pataliputra and Vaishali
b) Rajgir
c) All
d) None - Fa-Hien noted the prosperity of Pataliputra under which ruler?
a) Chandragupta II
b) Samudragupta
c) Skandagupta
d) Kumaragupta - The traveler Itsing praised which Bihar university for its library?
a) Nalanda
b) Vikramshila
c) Odantapuri
d) All - The impact of Alexander’s invasion on Bihar was?
a) Cultural exchange
b) Political instability
c) Both
d) Minimal - Persian influence on Mauryan art in Bihar is seen in?
a) Pillars
b) Caves
c) Stupas
d) All - The ancient Bihar was known for which crop in Vedic times?
a) Rice
b) Wheat
c) Barley
d) Millet - The Mauryan economy in Bihar included state farms called?
a) Sita lands
b) Crown lands
c) Both
d) None - Gupta period Bihar saw the issue of which type of coins?
a) Gold dinars
b) Silver rupees
c) Copper
d) All - The Pala economy relied on trade with which region?
a) Southeast Asia
b) China
c) Both
d) Europe - Ancient Bihar’s iron mines were located in which area?
a) South Bihar
b) Chota Nagpur
c) Both
d) North Bihar - The ancient port of Tamralipti near Bihar was used for trade with?
a) Southeast Asia
b) Rome
c) Both
d) China - The Nanda dynasty’s irrigation system in Bihar included?
a) Canals
b) Wells
c) Tanks
d) All - Gupta Bihar’s land grants led to?
a) Feudalism
b) Centralization
c) Trade boost
d) None - Mauryan Bihar had guilds called?
a) Srenis
b) Nigamas
c) Both
d) None
BPSC Zone

Made with cracktarget.com


Leave a reply to BPSC 71st (2025) 60 Days 60 Tests – cracktarget Cancel reply